Everything you need to know about stem cells
What are stem cells, and what makes them so unique? What are the different types of stem cells, and how have they impacted modern medical science? Here is us answering all your questions about stem cells.
Simple chemical reactions encapsulated into a lipid sphere could have been the origin of the first cell more than 3 billion years ago on a young Earth. From then on, evolution has driven life into a complicated coordination of different types of cells, tissues, organs, organisms, populations and the biosphere. Although, we now understand much more about mechanisms driving life, we are still in the dark about many of the intricate details of these mechanisms. Research is still ongoing. Here, you will find research stories that try to understand the complexity of life in its various forms.

What are stem cells, and what makes them so unique? What are the different types of stem cells, and how have they impacted modern medical science? Here is us answering all your questions about stem cells.

How does the skin seamlessly stretch and expand itself around a growing foetus as pregnancy progresses? The answer lies in the skin proteins - collagen and elastin.

With vaccines being a medical success for over a century now, could we now use the same principle in treating cancer? - The answer is yes.
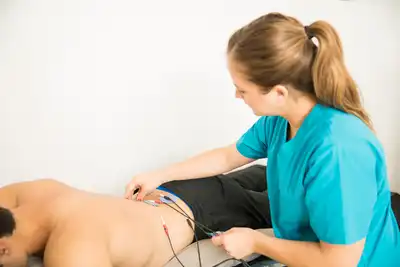
Chronic pain causes life-long distress in millions of patients worldwide. An upcoming therapeutic strategy called the Scrambler Therapy may provide fresh hope.

Latest research in T cell cancer immunotherapy might hold promise for patients with solid tumours.
Scientists discover a new way by which Salmonella develop antibiotic resistance.

Studies show that learning to play music can change the structure of the brain and can be beneficial for everyone, from young children to the aged.

We humans seem to share a unique bond with dogs. Here are some science-backed reasons as to why this might be so.
Scientists show that these aquatic, unicellular organisms can multiply by just eating viruses.

The bubonic plague took millions of lives in the 14th century, sparing only a lucky few. However, studies now show that surviving the plague may have come at an unfortunate cost.
Scientists hack the immune system to treat the autoimmune disease – systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), also called Lupus.
Our skin, being the outermost layer of our body, is very susceptible to wounds. Here we discuss the sophisticated mechanism by which our body heals these wounds.

Scientists studying sleeping spiders find that they sleep very similar to humans. This reveals that sleep must have a very important role in evolution.
Neither a plant nor an animal, fungi are very unique organisms. The black bread mould is especially one such fungus.
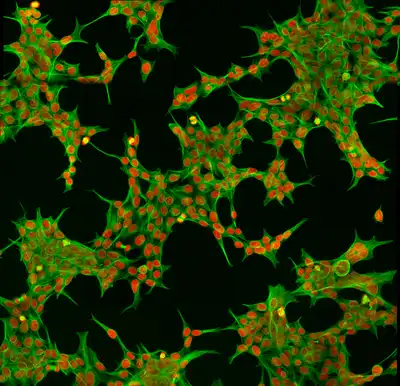
When it comes to our cells, staying in shape is very important. This is because the shape of our cells can ultimately control their function.

The cunning, yet genius trapping mechanisms in carnivorous plants.
Why developing a vaccine against HIV has proven so difficult and the 3 promising HIV vaccine candidates to look out for.

From chronic inflammatory pain to migraine, the discovery behind this year’s Nobel Prize could improve the quality of millions of lives.

Converting simple sugary solutions into delicious, syrupy honey, bees can indeed be considered master chefs!

Here, I discuss three interesting strategies proposed by scientists that have the potential to permanently cure type 2 diabetes.

Dogs have contrasting visual abilities when compared to humans.

The role of telomerase in telomere maintenance and ageing.
Researchers recruited hundreds of dogs to a 'theory of mind' experiment, and determined that dogs were more likely to use their visual experience over cues from lying humans when looking for treats.

Researchers identified patterns of brain maturation in worms using electron microscopy, providing insights into brain development in humans.